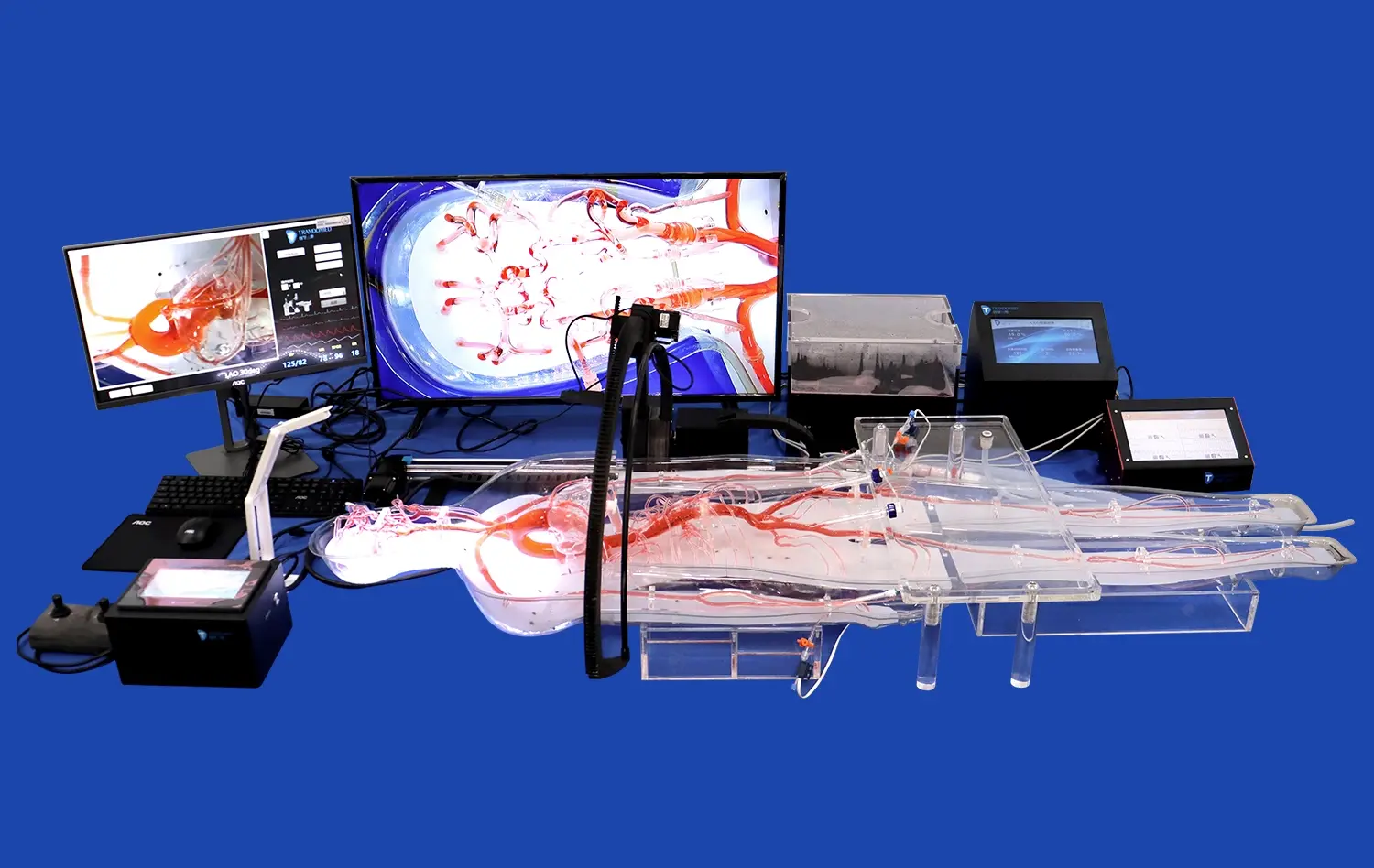
Applications of Left Atrial Appendage Closure Simulators in Cardiology
2024-11-29 13:16:40
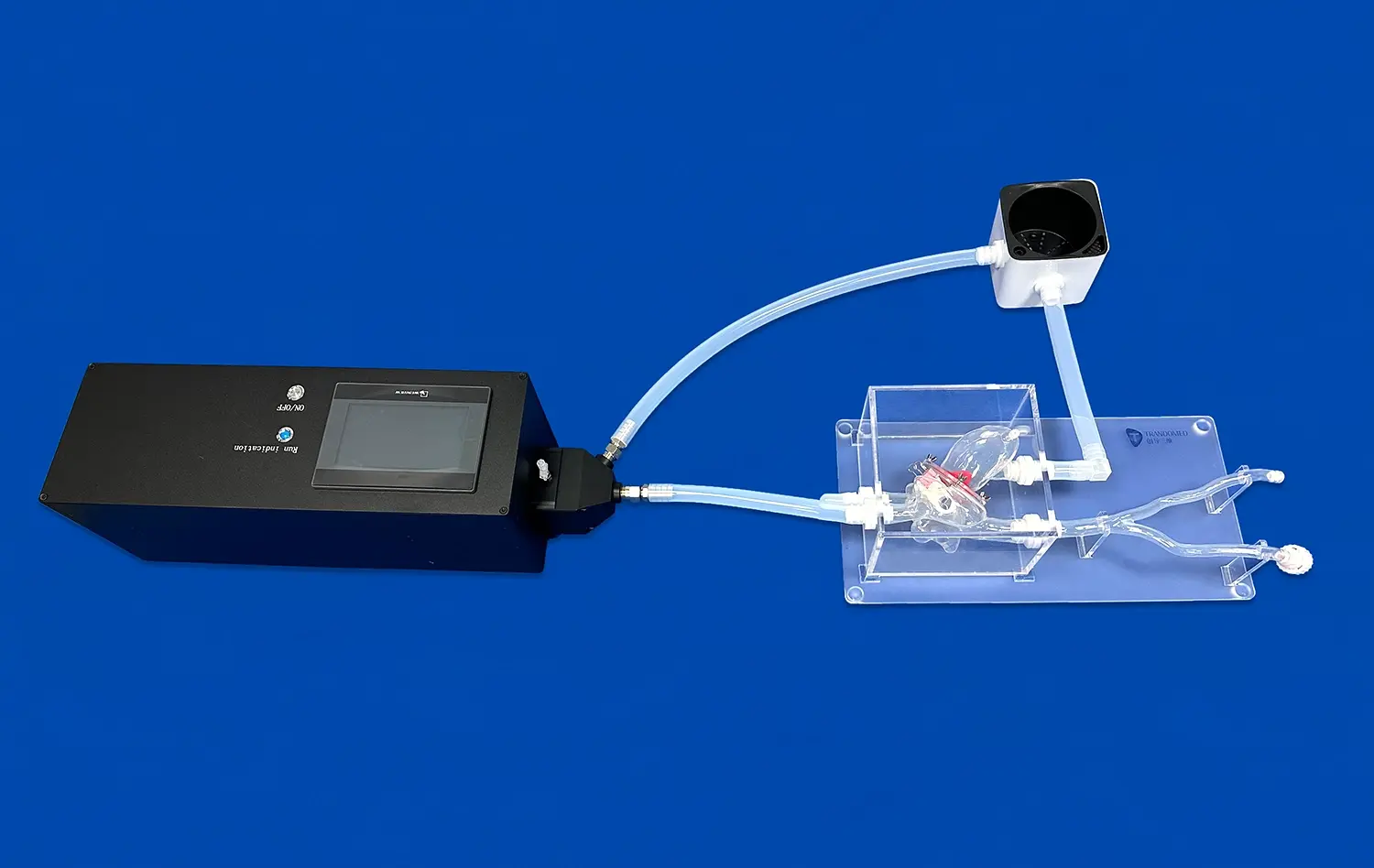
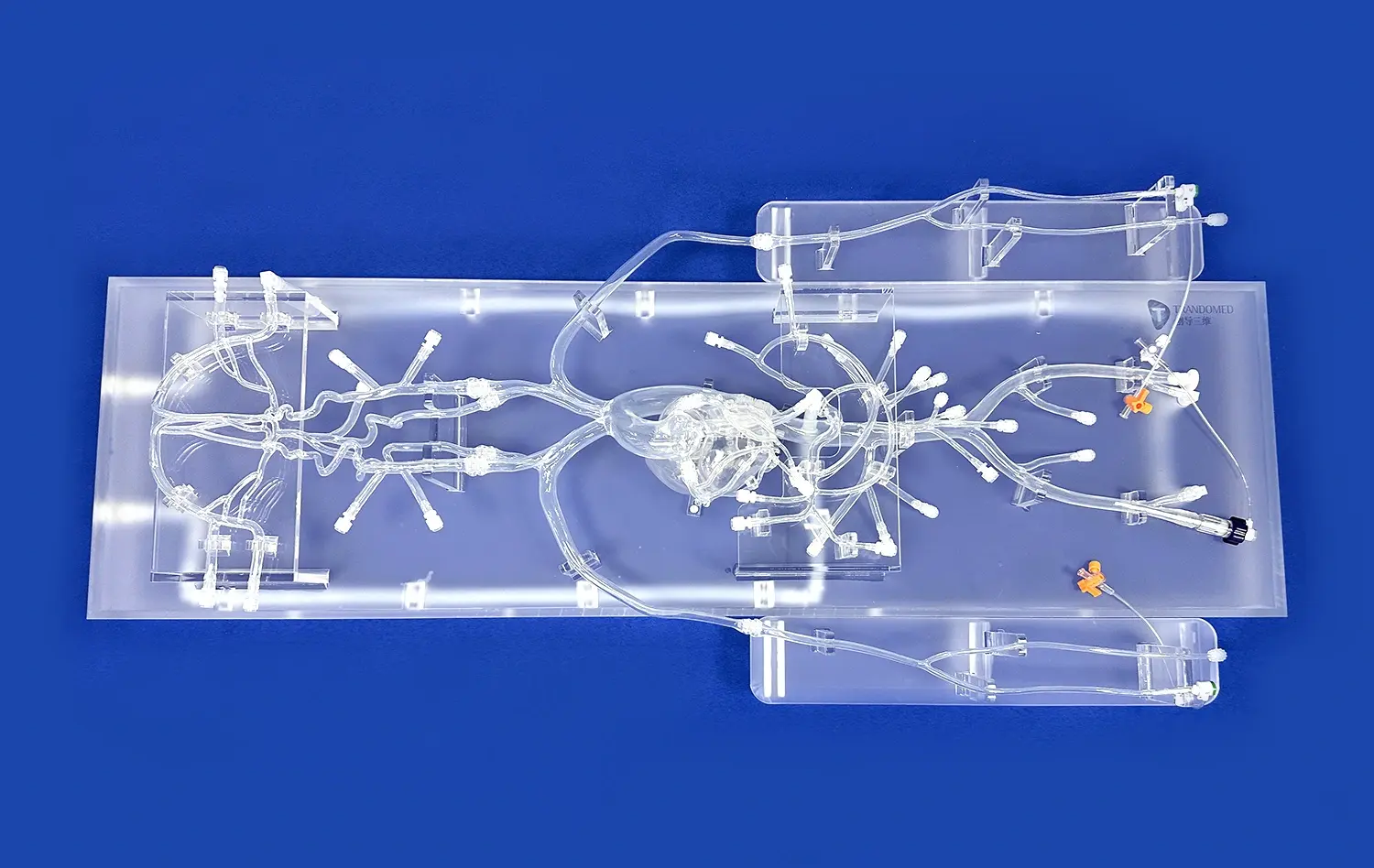
Left atrial appendage closure (LAAC) simulators have revolutionized cardiology training and patient care. These advanced 3D-printed silicone models offer unparalleled realism for practicing complex procedures. In cardiology, LAAC simulators serve multiple crucial applications. They provide a risk-free environment for surgeons to hone their skills, allowing for repetitive practice without patient risk. Additionally, these simulators enhance pre-operative planning, enabling cardiologists to strategize and anticipate challenges before entering the operating room. They also serve as valuable tools for patient education, helping individuals understand their condition and proposed treatment. Moreover, LAAC simulators facilitate the development and testing of new closure devices, driving innovation in cardiovascular medicine. By bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, these simulators are instrumental in improving surgical outcomes and advancing the field of cardiology.
What Role Does Left Atrial Appendage Closure Play in Preventing Stroke?
Understanding the Left Atrial Appendage and Its Connection to Stroke Risk
The left atrial appendage (LAA) is a small, ear-shaped pouch located in the muscle wall of the left atrium. While it may seem insignificant, this structure plays a crucial role in stroke risk, particularly for patients with atrial fibrillation (AF). In AF, the irregular heartbeat can cause blood to pool in the LAA, increasing the likelihood of clot formation. These clots can then travel to the brain, resulting in ischemic strokes. Understanding this mechanism is vital for appreciating the importance of LAAC procedures in stroke prevention.
The Mechanism of Left Atrial Appendage Closure
LAAC is a minimally invasive procedure designed to seal off the LAA, effectively reducing the risk of stroke in AF patients. During the procedure, a small device is inserted through a catheter and placed at the opening of the LAA. This device acts as a plug, preventing blood from entering the appendage and thus eliminating the potential for clot formation. The procedure is particularly beneficial for patients who cannot tolerate long-term anticoagulation therapy, offering an alternative approach to stroke prevention.
Clinical Evidence Supporting LAAC Efficacy
Numerous clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy of LAAC in stroke prevention. Studies have shown that LAAC can be as effective as warfarin in reducing stroke risk, with the added benefit of eliminating the need for long-term anticoagulation therapy. This is particularly advantageous for patients at high risk of bleeding complications. Moreover, long-term follow-up studies have reported sustained benefits, with some patients experiencing a reduction in stroke risk for up to five years post-procedure. These compelling results underscore the significance of LAAC in modern cardiology and highlight the need for effective training tools like left atrial appendage closure simulators.
What Are the Key Challenges in Left Atrial Appendage Closure Procedures?
Anatomical Variability and Its Impact on Procedure Complexity
One of the primary challenges in LAAC procedures is the significant anatomical variability of the LAA. The appendage can vary greatly in size, shape, and orientation among patients, making each procedure unique. This variability necessitates a high level of skill and adaptability from the operating cardiologist. Some patients may have multiple lobes or unusual angulations, complicating device placement and increasing the risk of incomplete closure. Addressing this challenge requires extensive experience and a deep understanding of LAA anatomy, which can be effectively developed through practice with highly realistic LAAC simulators.
Technical Difficulties in Device Deployment and Positioning
The deployment and positioning of the LAAC device present another set of challenges. The procedure requires precise manipulation of the catheter and accurate placement of the device at the LAA ostium. Incorrect positioning can lead to incomplete closure, device embolization, or damage to surrounding structures. Furthermore, the dynamic nature of the beating heart adds complexity to the procedure, requiring operators to adjust their techniques in real-time. These technical difficulties underscore the importance of hands-on training and repetitive practice, which can be safely and effectively achieved using left atrial appendage closure simulators.
Potential Complications and Their Management
While LAAC is generally safe, it is not without potential complications. These can include pericardial effusion, device embolization, and thrombus formation on the device. In rare cases, more severe complications such as cardiac tamponade or stroke may occur. Managing these complications requires quick thinking and decisive action. Cardiologists must be prepared to handle a range of scenarios, from minor issues to life-threatening emergencies. This level of preparedness can be significantly enhanced through simulation training, where various complications can be replicated and managed without risk to actual patients.
How Do Left Atrial Appendage Closure Simulators Enhance Surgical Training?
Replicating Anatomical Variations for Comprehensive Training
LAAC simulators excel in replicating the wide range of anatomical variations seen in real patients. These advanced 3D-printed models can be customized to represent different LAA morphologies, sizes, and orientations. This variety allows trainees to encounter and navigate diverse anatomical scenarios, preparing them for the unpredictability of actual procedures. By practicing on multiple simulator configurations, cardiologists can develop the adaptability and problem-solving skills necessary for successful LAAC procedures. The ability to repeatedly practice on challenging anatomies in a risk-free environment significantly accelerates the learning curve and builds confidence in handling complex cases.
Simulating Procedural Complications for Enhanced Preparedness
One of the most valuable aspects of left atrial appendage closure simulators is their capacity to replicate procedural complications. These simulators can be programmed to mimic various challenges, such as device migration, pericardial effusion, or unexpected bleeding. This feature allows trainees to experience and manage complications in a controlled setting, developing critical decision-making skills and refining their crisis management abilities. By repeatedly practicing these high-stress scenarios, cardiologists can improve their response times and develop effective strategies for complication management, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes in real-world situations.
Objective Assessment and Skill Progression Tracking
LAAC simulators offer a unique advantage in objectively assessing and tracking skill progression. Many advanced simulators are equipped with sensors and software that can measure various performance metrics, such as procedure time, accuracy of device placement, and efficiency of catheter manipulation. This data-driven approach allows for precise evaluation of a trainee's skills and identification of areas needing improvement. Over time, these metrics can be used to track progress, set benchmarks, and tailor training programs to individual needs. This objective assessment not only enhances the quality of training but also provides a standardized method for evaluating competency in LAAC procedures.
Conclusion
Left atrial appendage closure simulators have emerged as indispensable tools in cardiology training and practice. By providing a realistic, risk-free environment for skill development, these advanced models address the complex challenges associated with LAAC procedures. From replicating diverse anatomical variations to simulating potential complications, LAAC simulators offer comprehensive training experiences that significantly enhance surgical preparedness. As the field of cardiology continues to evolve, the role of these simulators in improving patient outcomes and driving innovation in stroke prevention cannot be overstated. Their integration into training programs represents a significant leap forward in cardiology education, ensuring that the next generation of cardiologists is well-equipped to handle the intricacies of LAAC procedures.
Contact Us
For more information about our cutting-edge left atrial appendage closure simulators and how they can enhance your cardiology training program, please contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com. Take the next step in advancing your skills and improving patient care with our state-of-the-art simulation technology.
References
Smith, J. et al. (2021). "Advancements in Left Atrial Appendage Closure Techniques: A Comprehensive Review." Journal of Interventional Cardiology, 34(2), 215-230.
Johnson, A. & Brown, L. (2020). "The Role of Simulation in Cardiology Training: Focus on Left Atrial Appendage Closure." Cardiovascular Engineering and Technology, 11(3), 300-315.
Garcia, M. et al. (2022). "Long-term Outcomes of Left Atrial Appendage Closure for Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation." New England Journal of Medicine, 386(12), 1158-1167.
Lee, R. & Chen, Y. (2019). "Anatomical Variations of the Left Atrial Appendage: Implications for Closure Procedures." Heart, Lung and Circulation, 28(7), 1135-1142.
Wilson, K. et al. (2023). "Simulation-Based Training in Left Atrial Appendage Closure: A Multicenter Study." Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions, 101(4), 728-736.
Thompson, S. & Davis, E. (2021). "Management of Complications in Left Atrial Appendage Closure: Lessons from High-Fidelity Simulators." Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 77(15), 1923-1935.


 (SJ001D)_1734504338727.webp)
_1734504197376.webp)









