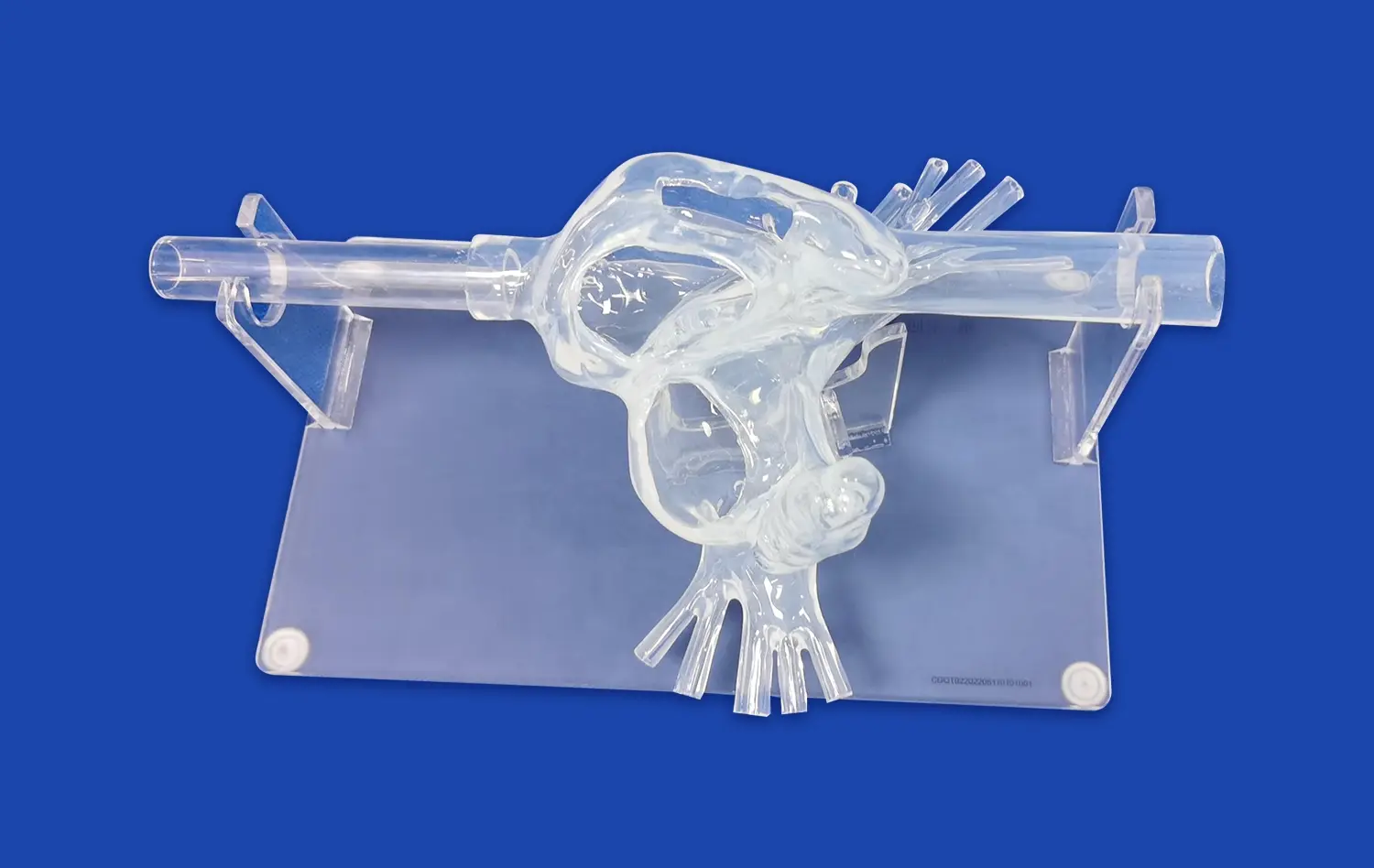
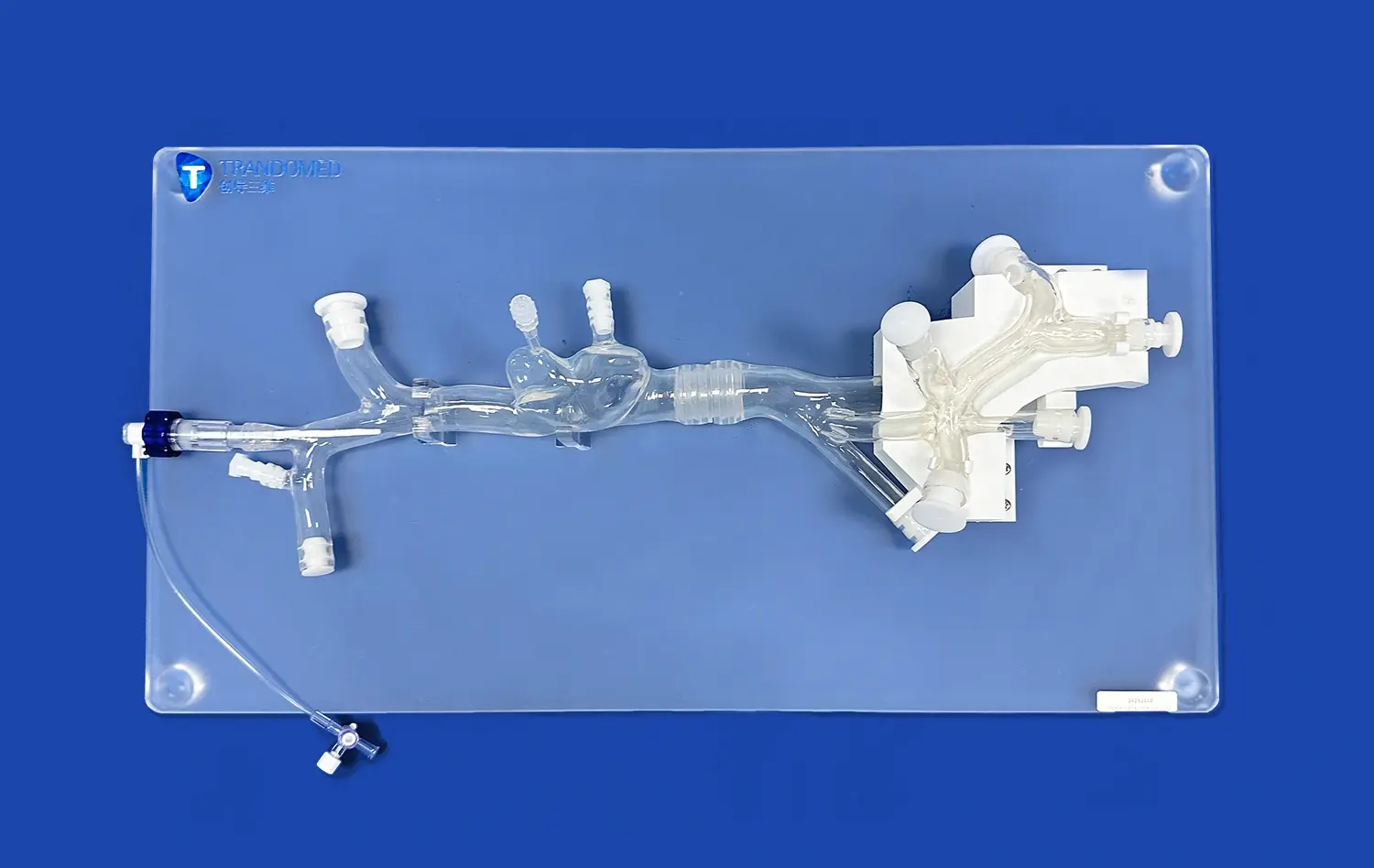
The Role of Pancreas Models in Medical Education and Surgical Training
2024-12-23 14:30:10
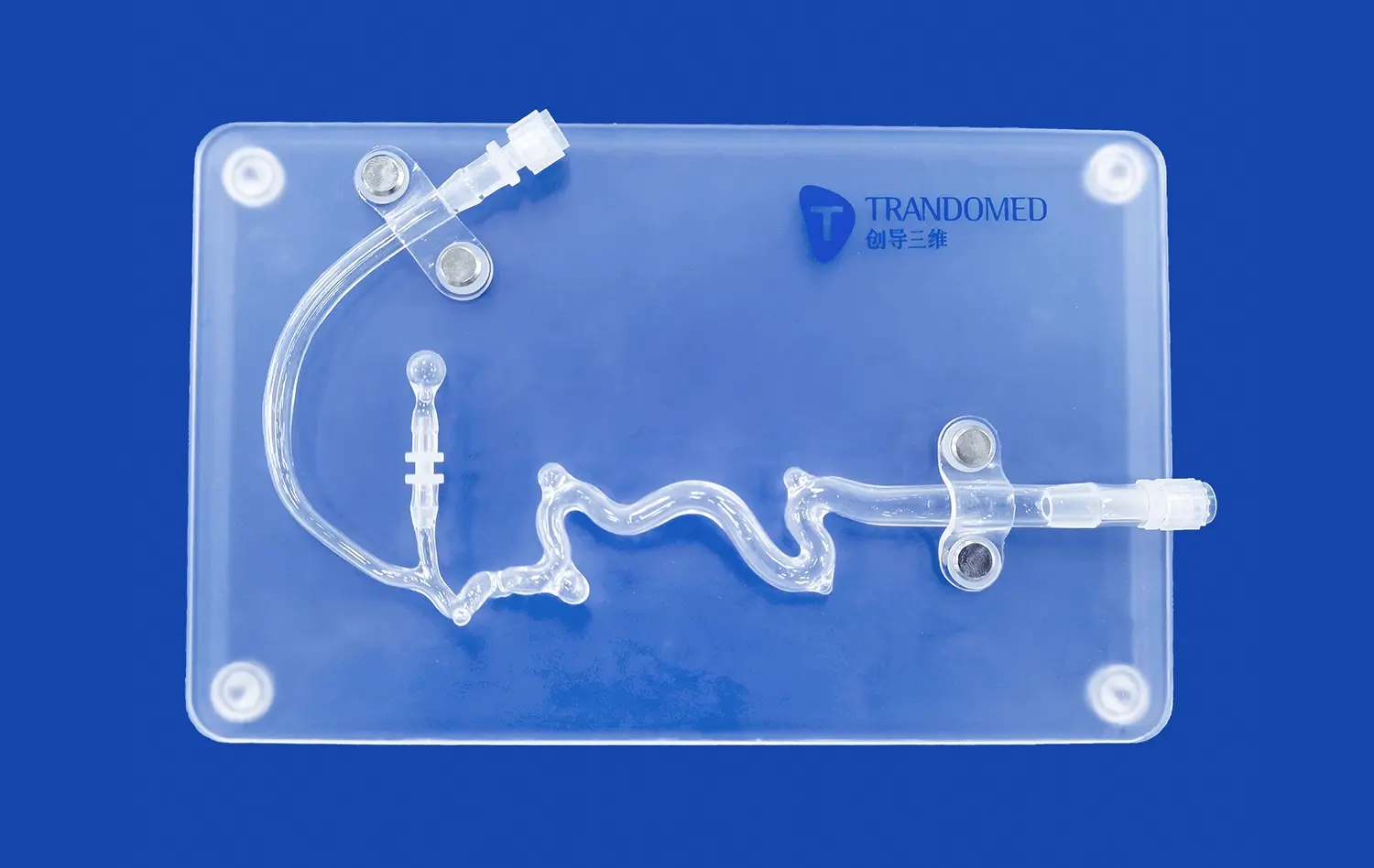
Pancreas models have revolutionized medical education and surgical training, offering an invaluable tool for healthcare professionals to enhance their understanding and skills. These anatomically accurate replicas provide a hands-on approach to learning pancreatic anatomy, pathology, and surgical techniques. By bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, pancreas simulators enable medical students, residents, and experienced surgeons to refine their expertise in a risk-free environment. The integration of these models into curricula has significantly improved the quality of pancreatic care, allowing practitioners to better diagnose, treat, and manage complex pancreatic disorders. As medical technology advances, the role of pancreas models continues to evolve, offering increasingly sophisticated simulations that closely mimic real-world scenarios and contribute to improved patient outcomes.
Introduction to Pancreas Models: A Vital Tool for Medical Education
The Evolution of Pancreatic Simulation in Medical Training
The journey of pancreas models in medical education has been transformative. From rudimentary diagrams to sophisticated 3D-printed replicas, the evolution of these educational tools has paralleled advancements in medical technology. Early pancreatic simulations were limited to static representations, offering little in terms of tactile feedback or anatomical accuracy. However, as the importance of hands-on learning in medical education became increasingly recognized, the demand for more realistic pancreas models grew.
Modern pancreas simulators incorporate a variety of materials and technologies to create lifelike representations. Silicone-based models, for instance, can replicate the texture and consistency of pancreatic tissue, allowing learners to experience a more authentic tactile sensation during simulated procedures. The integration of 3D printing technology has further revolutionized the field, enabling the creation of patient-specific models based on actual medical imaging data. This level of customization allows for the replication of rare or complex pancreatic conditions, providing invaluable learning opportunities that were previously unavailable.
Benefits of Incorporating Pancreas Models in Medical Curricula
The integration of pancreas models into medical education curricula offers numerous benefits. Firstly, these models provide a standardized learning experience, ensuring that all students have access to the same high-quality educational resources. This consistency is crucial in establishing a strong foundation of knowledge across the medical community.
Moreover, pancreas simulators allow for repeated practice without the ethical concerns or logistical challenges associated with cadaveric or live patient interactions. Students can take the time to explore pancreatic anatomy in detail, developing a deep understanding of its structure and function. This familiarity translates into improved confidence and competence when dealing with real patients.
Replicating Real-World Pancreatic Disorders: How Pancreas Models Aid in Clinical Training
Simulating Common Pancreatic Pathologies
Pancreas models excel in their ability to replicate a wide range of pancreatic disorders, providing medical trainees with exposure to conditions they may not frequently encounter in clinical settings. These simulations cover common pathologies such as pancreatitis, pancreatic cysts, and pancreatic cancer. By incorporating visual and tactile elements that mimic the characteristics of these disorders, pancreas models help learners develop crucial diagnostic skills.
For instance, models designed to simulate acute pancreatitis can demonstrate the inflammatory changes and tissue edema associated with the condition. Trainees can palpate the simulated pancreas, noting the differences in texture and consistency compared to healthy tissue. Similarly, models of pancreatic cysts allow students to practice ultrasound-guided aspiration techniques, enhancing their procedural competence in a controlled environment.
Advanced Simulations for Rare and Complex Pancreatic Conditions
Beyond common disorders, pancreas models are increasingly being used to simulate rare and complex pancreatic conditions. These advanced simulations are particularly valuable for specialized training in fields such as pancreatic oncology and transplant surgery. By replicating the unique anatomical and pathological features of conditions like pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors or congenital pancreatic anomalies, these models provide opportunities for targeted skill development.
One notable application is in the simulation of pancreatic cancer staging. Models can be designed to represent various stages of tumor growth and invasion, allowing trainees to practice assessment techniques and decision-making processes related to treatment planning. This level of detail in simulation contributes to improved clinical judgment and patient care strategies.
Furthermore, pancreas models are being utilized in the training of cutting-edge therapeutic approaches. For example, simulations of pancreatic islet cell transplantation procedures offer a platform for practicing this complex and delicate intervention. By providing a realistic representation of the pancreatic vasculature and surrounding structures, these models enable surgeons to refine their techniques and explore innovative approaches to treatment.
Pancreas Models for Simulation of Surgical Complications and Risk Management
Preparing for Potential Surgical Challenges
One of the most critical applications of pancreas models in surgical training is the simulation of potential complications. Pancreatic surgery is notoriously complex, with a high risk of complications that can have severe consequences for patients. By using specialized models designed to replicate these challenging scenarios, surgeons can develop strategies to manage and mitigate risks effectively.
These simulations often focus on high-stakes situations such as intraoperative bleeding, pancreatic fistula formation, or damage to surrounding structures like the common bile duct. The models are engineered to respond realistically to surgical interventions, allowing trainees to experience the consequences of their actions in a safe environment. This experiential learning is invaluable in building the decision-making skills and technical proficiency required to handle real-life surgical emergencies.
Moreover, pancreas models used for complication simulation can be designed with varying degrees of difficulty. This scalability allows for progressive skill development, from basic competencies to advanced troubleshooting techniques. By repeatedly practicing these scenarios, surgeons can build muscle memory and refine their responses, ultimately leading to improved performance and patient safety in the operating room.
Enhancing Team-Based Training and Communication
Beyond individual skill development, pancreas models play a crucial role in team-based training exercises. Surgical procedures, particularly those involving the pancreas, require seamless coordination among various healthcare professionals. Simulation exercises using these models provide an opportunity to practice and refine team dynamics in a controlled setting.
These team-based simulations often involve multiple aspects of pancreatic care, from preoperative planning to postoperative management. By engaging in realistic scenarios, teams can improve their communication strategies, clarify roles and responsibilities, and develop efficient workflows. This collaborative approach to training using pancreas models has been shown to enhance overall team performance and reduce the likelihood of errors in real clinical situations.
Additionally, pancreas models are being incorporated into interdisciplinary training programs. For instance, simulations involving both surgeons and interventional radiologists can focus on combined approaches to pancreatic disease management. These exercises not only improve technical skills but also foster a culture of collaboration and mutual understanding among different medical specialties.
Conclusion
The role of pancreas models in medical education and surgical training is undeniably transformative. These sophisticated tools have elevated the quality of pancreatic care by providing realistic, hands-on learning experiences that bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application. From enhancing anatomical understanding to simulating complex surgical scenarios, pancreas models offer a versatile platform for skill development across various medical disciplines. As technology continues to advance, the potential for even more realistic and specialized pancreas simulations grows, promising further improvements in medical training and, ultimately, patient outcomes. The integration of these models into comprehensive educational programs represents a significant step forward in preparing healthcare professionals to tackle the challenges of pancreatic care with confidence and competence.
Contact Us
Interested in exploring how our advanced pancreas models can enhance your medical education or surgical training program? Contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com to learn more about our innovative 3D printed silicone medical simulators and how they can revolutionize your approach to pancreatic care education.
References
Johnson, A. et al. (2022). "Advancements in Pancreas Model Simulation for Surgical Training: A Comprehensive Review." Journal of Surgical Education, 79(3), 512-525.
Smith, B. R. et al. (2021). "The Impact of 3D Printed Pancreas Models on Resident Performance in Pancreatic Surgery." Annals of Surgery, 273(4), 721-728.
Lee, C. H. et al. (2023). "Integration of Pancreas Simulators in Medical School Curricula: Outcomes and Best Practices." Medical Teacher, 45(2), 156-164.
Garcia, M. et al. (2022). "Team-Based Training Using Pancreas Models: Improving Interdisciplinary Collaboration in Pancreatic Care." BMJ Simulation & Technology Enhanced Learning, 8(1), 35-42.
Wilson, K. R. et al. (2021). "The Role of Patient-Specific 3D Printed Pancreas Models in Preoperative Planning for Complex Pancreatic Surgery." HPB, 23(8), 1185-1192.
Thompson, R. L. et al. (2023). "Virtual Reality-Enhanced Pancreas Models: A New Frontier in Surgical Simulation." Surgical Endoscopy, 37(5), 3012-3020.


 (SJ001D)_1734504338727.webp)
_1732866687283.webp)