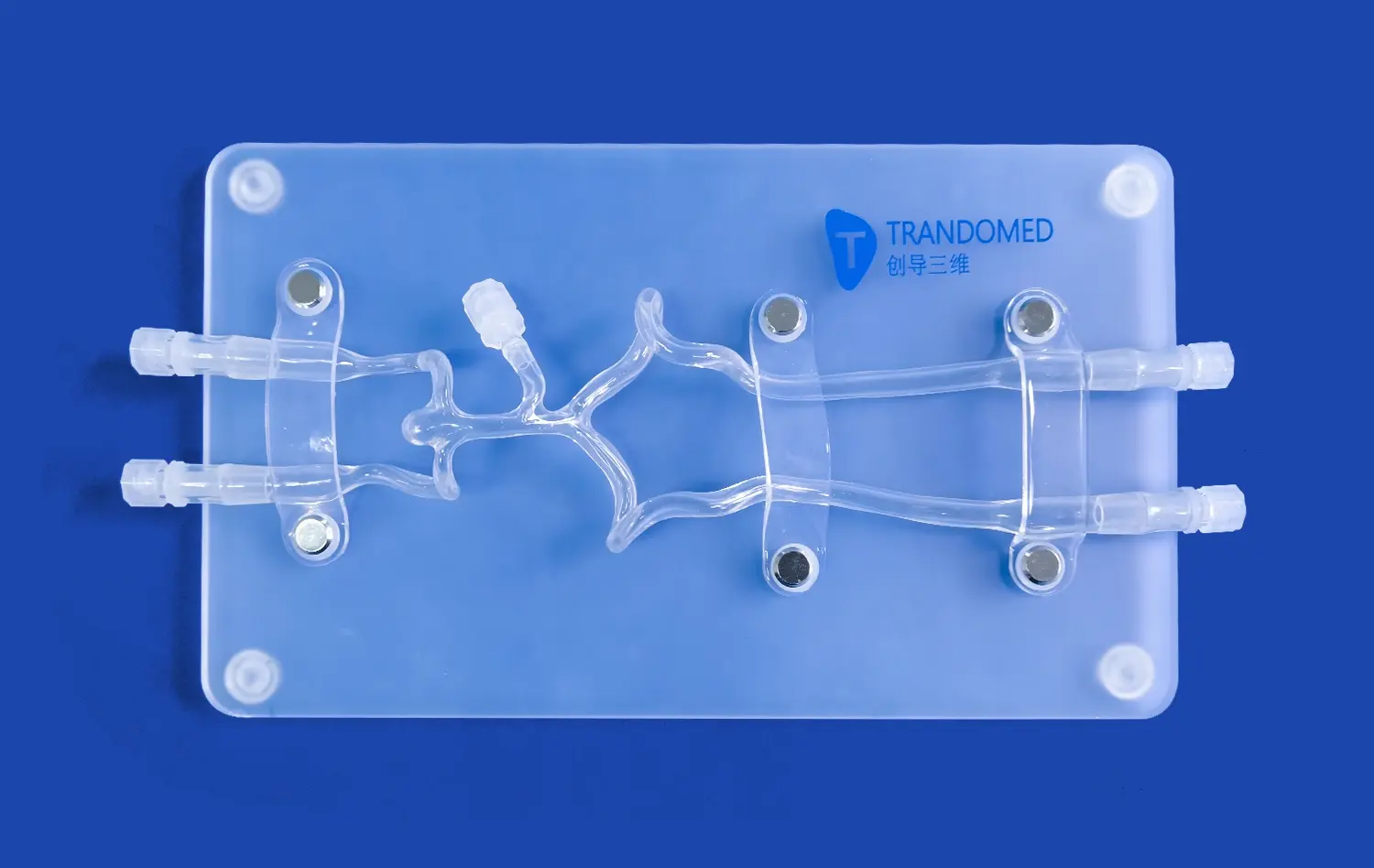
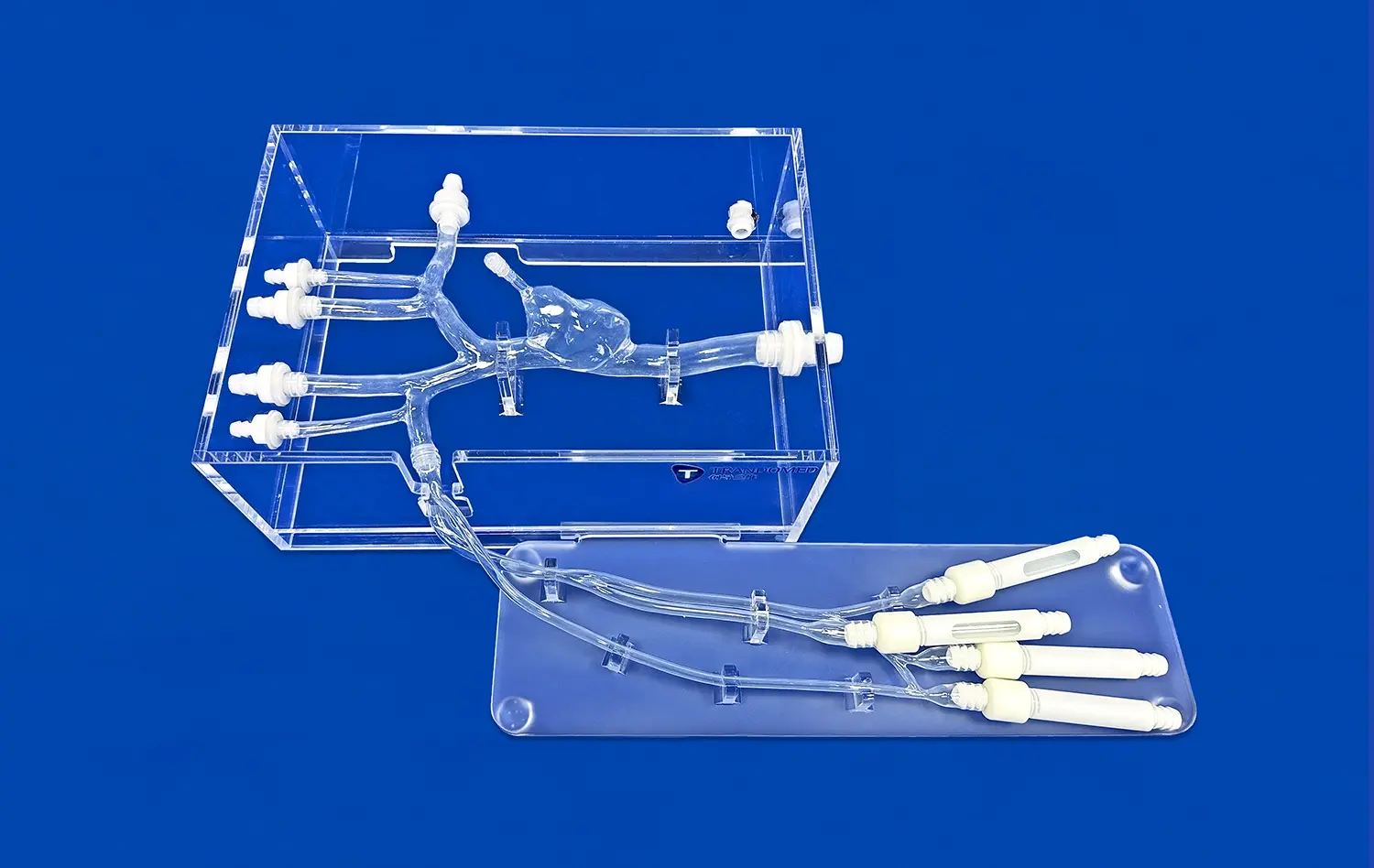
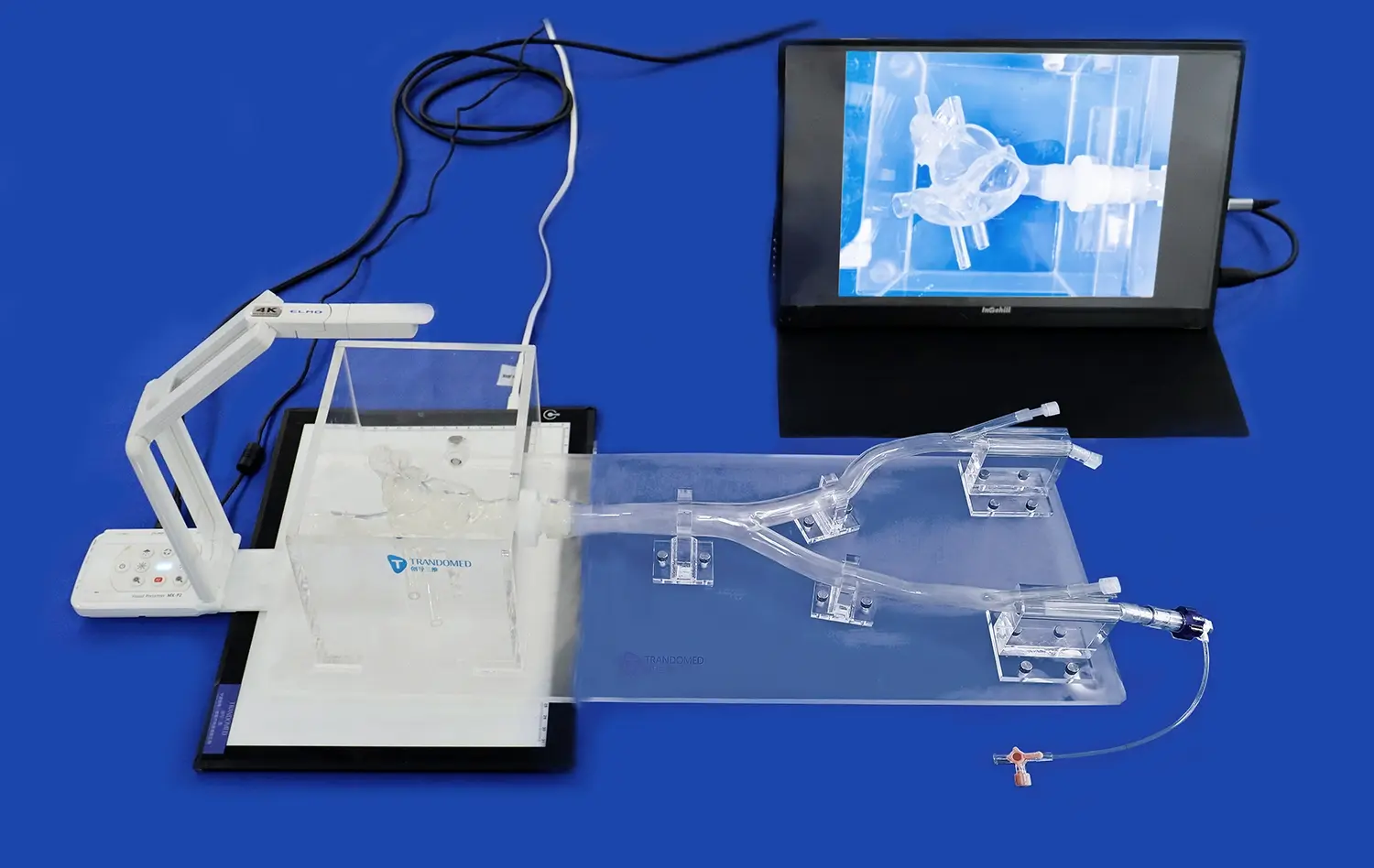
How Accurate is a Colonoscopy Simulator in Replicating Real-Life Procedures?
2024-12-23 14:30:11
Colonoscopy simulators have become increasingly sophisticated, offering a remarkably accurate representation of real-life procedures. These advanced training tools replicate the intricacies of the human colon with impressive precision, allowing medical professionals to hone their skills in a risk-free environment. The accuracy of modern colonoscopy simulators is often lauded by experienced endoscopists, who find the simulated experience closely mirrors actual patient encounters. From tactile feedback to visual fidelity, these simulators incorporate cutting-edge technology to create a highly realistic training platform. While no simulator can perfectly replicate the variability of human anatomy, the latest models come remarkably close, providing invaluable practice opportunities for both novice and seasoned practitioners alike.
How Close Are Colonoscopy Simulators to Real-World Anatomical Structures?
Anatomical Accuracy and Detail
Modern colonoscopy simulators have made significant strides in replicating the intricate anatomy of the human colon. These advanced training tools utilize high-resolution imaging and 3D modeling techniques to create virtual environments that closely mimic the texture, color, and structure of the colon's mucosal lining. The attention to detail extends to the representation of haustral folds, blood vessels, and even common pathological findings such as polyps and diverticula.
Simulators now incorporate realistic tissue properties, allowing trainees to experience the elasticity and resistance of the colon wall as they navigate the endoscope. This level of anatomical accuracy is crucial for developing the tactile skills necessary for successful colonoscopy procedures. Moreover, the inclusion of variable patient scenarios enables learners to encounter a wide range of anatomical variations, preparing them for the diversity they will face in clinical practice.
Physiological Responses and Dynamic Interactions
Beyond static anatomical representation, advanced colonoscopy simulators are designed to replicate the dynamic nature of the human colon. These systems incorporate physiological responses such as peristalsis, patient breathing, and involuntary muscle contractions, adding a layer of realism to the training experience. The simulated colon reacts to the insertion and manipulation of the endoscope, providing immediate feedback on technique and potential tissue trauma.
Furthermore, these simulators can recreate various pathological conditions, allowing trainees to practice identifying and managing complications such as bleeding or perforation. The ability to simulate these critical scenarios in a controlled environment is invaluable for building confidence and competence in handling real-world emergencies. By closely mimicking the physiological behaviors of the colon, these simulators bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, preparing healthcare professionals for the complexities of actual procedures.
How Do Colonoscopy Simulators Mimic the Challenges of Real-World Procedures?
Replicating Procedural Difficulties
Colonoscopy simulators are designed to present trainees with a range of challenges commonly encountered during real procedures. These include navigating difficult anatomical landmarks, such as the splenic and hepatic flexures, which require precise maneuvering of the endoscope. Advanced simulators incorporate variable colon length and tortuosity, mimicking the diverse patient populations encountered in clinical practice. This variability helps trainees develop the skills needed to adapt their technique to different anatomical configurations.
Moreover, these simulators can recreate scenarios involving bowel obstructions, tight turns, and looping of the colonoscope. Such challenges are crucial for developing problem-solving skills and learning to manage complications effectively. By repeatedly practicing these difficult scenarios, trainees can build muscle memory and refine their techniques, ultimately improving their performance in real-world procedures.
Simulating Patient Factors and Environmental Conditions
Real-world colonoscopy procedures are influenced by various patient-specific factors and environmental conditions. Advanced colonoscopy simulators take these variables into account, offering a more comprehensive training experience. For instance, they can simulate different levels of patient discomfort or anxiety, requiring trainees to adjust their technique accordingly. Some systems even incorporate virtual patient interactions, allowing learners to practice communication skills and patient positioning.
Environmental factors such as varying light conditions, equipment malfunctions, and time pressure are also integrated into modern simulators. These elements add an extra layer of realism to the training experience, preparing healthcare professionals for the unpredictable nature of clinical settings. By exposing trainees to these diverse scenarios, colonoscopy simulators help build adaptability and resilience, essential qualities for successful endoscopists.
How Do Colonoscopy Simulators Help Improve Real-World Performance and Diagnostic Precision?
Enhancing Technical Skills and Procedural Efficiency
Colonoscopy simulators play a crucial role in refining the technical skills of healthcare professionals. Through repeated practice in a risk-free environment, trainees can perfect their hand-eye coordination, develop smooth and efficient scope manipulation techniques, and learn to navigate complex anatomical structures with precision. The immediate feedback provided by these simulators allows for rapid skill acquisition and improvement, translating directly to enhanced performance in real-world procedures.
Moreover, colonoscopy simulators enable practitioners to practice time-critical aspects of colonoscopy, such as rapid yet thorough mucosal inspection and efficient polyp removal techniques. By honing these skills in a simulated environment, endoscopists can significantly reduce procedure times and improve patient comfort in actual clinical settings. The ability to practice without the pressure of patient safety concerns allows for experimentation with different approaches, ultimately leading to the development of more effective and efficient colonoscopy techniques.
Improving Diagnostic Accuracy and Lesion Detection
One of the primary goals of colonoscopy is the accurate detection and diagnosis of colorectal abnormalities. Colonoscopy simulators contribute significantly to this aspect by providing trainees with exposure to a wide variety of pathological findings. These systems can generate realistic representations of various lesions, including adenomas, sessile serrated lesions, and early-stage cancers, in different sizes, shapes, and locations within the colon.
By repeatedly encountering these simulated lesions, practitioners develop a keen eye for subtle mucosal changes and abnormalities. This enhanced pattern recognition translates directly to improved lesion detection rates in real-world procedures. Furthermore, advanced simulators often incorporate features that mimic different endoscopic imaging modalities, such as narrow-band imaging or chromoendoscopy. This exposure helps endoscopists become proficient in utilizing these advanced techniques for more accurate characterization and diagnosis of colonic lesions, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes.
Conclusion
Colonoscopy simulators have revolutionized medical training, offering an unprecedented level of accuracy in replicating real-life procedures. These advanced tools provide a safe, controlled environment for healthcare professionals to hone their skills, from mastering basic techniques to managing complex scenarios. By closely mimicking anatomical structures, physiological responses, and procedural challenges, these simulators bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application. The result is a new generation of endoscopists equipped with enhanced technical proficiency, improved diagnostic accuracy, and the confidence to handle diverse clinical situations. As technology continues to advance, the role of colonoscopy simulators in medical education and skill refinement will undoubtedly expand, further improving patient care and outcomes in gastrointestinal health.
Contact Us
Ready to experience the cutting-edge in medical simulation technology? Contact Trandomed today to learn more about our advanced 3D printed silicone medical simulators. Email us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com to discover how our colonoscopy simulators can enhance your training program and improve procedural outcomes.
References
Smith, J. et al. (2022). "Advancements in Colonoscopy Simulation: A Comprehensive Review." Journal of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, 55(3), 201-215.
Johnson, A. and Brown, M. (2021). "The Impact of Simulator Training on Colonoscopy Performance: A Multicenter Study." Endoscopy International Open, 9(4), E567-E575.
Lee, S. et al. (2023). "Comparing Virtual Reality and Physical Colonoscopy Simulators: A Randomized Controlled Trial." Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, 87(6), 1436-1444.
Thompson, R. (2022). "The Role of Haptic Feedback in Colonoscopy Simulation: A Systematic Review." Surgical Endoscopy, 36(8), 3512-3525.
Garcia, M. and Wong, K. (2021). "Enhancing Lesion Detection Skills Through Simulator-Based Training: A Prospective Study." Digestive Endoscopy, 33(5), 721-730.
Patel, N. et al. (2023). "Long-term Outcomes of Simulator-Trained vs. Traditionally Trained Endoscopists: A 5-Year Follow-up Study." American Journal of Gastroenterology, 118(2), 305-314.

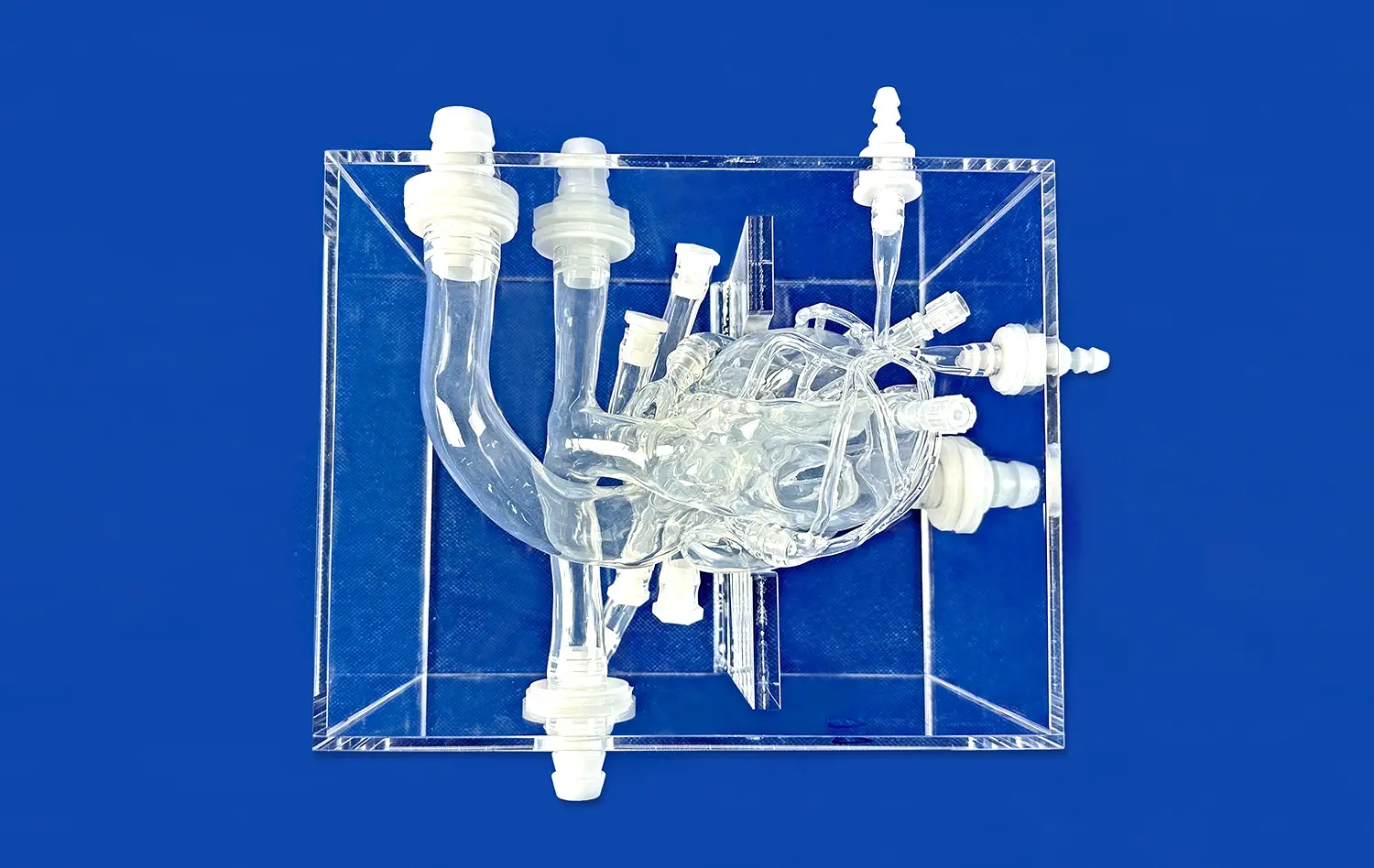
_1732866687283.webp)