How 3D Kidney Models Improve Medical Training for Renal Surgeons?
2024-12-30 16:46:48
3D kidney models have revolutionized medical training for renal surgeons, offering unprecedented opportunities to enhance surgical skills and improve patient outcomes. These anatomically accurate replicas provide a tangible, hands-on approach to learning complex renal structures and pathologies. By integrating advanced 3D printing technology with medical imaging data, these models allow surgeons to visualize, practice, and perfect intricate procedures before entering the operating room. This innovative approach bridges the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, enabling surgeons to gain confidence and proficiency in a risk-free environment. The use of 3D kidney models in medical education has shown to significantly reduce surgical errors, decrease operative times, and improve overall surgical outcomes, making them an invaluable tool in the training of both novice and experienced renal surgeons.
How Do 3D Kidney Models Enhance the Understanding of Kidney Anatomy for Surgeons?
Detailed Anatomical Representation
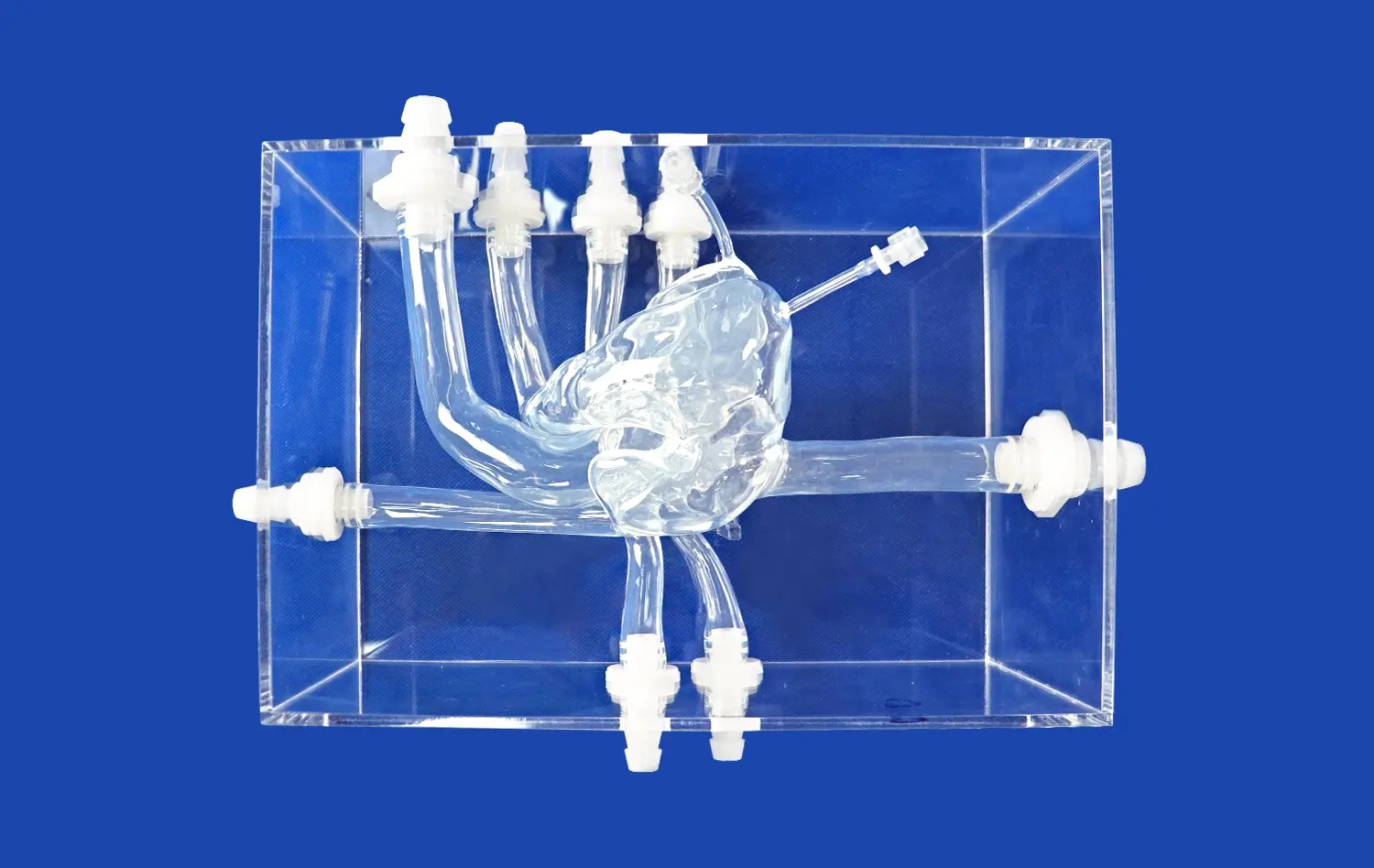
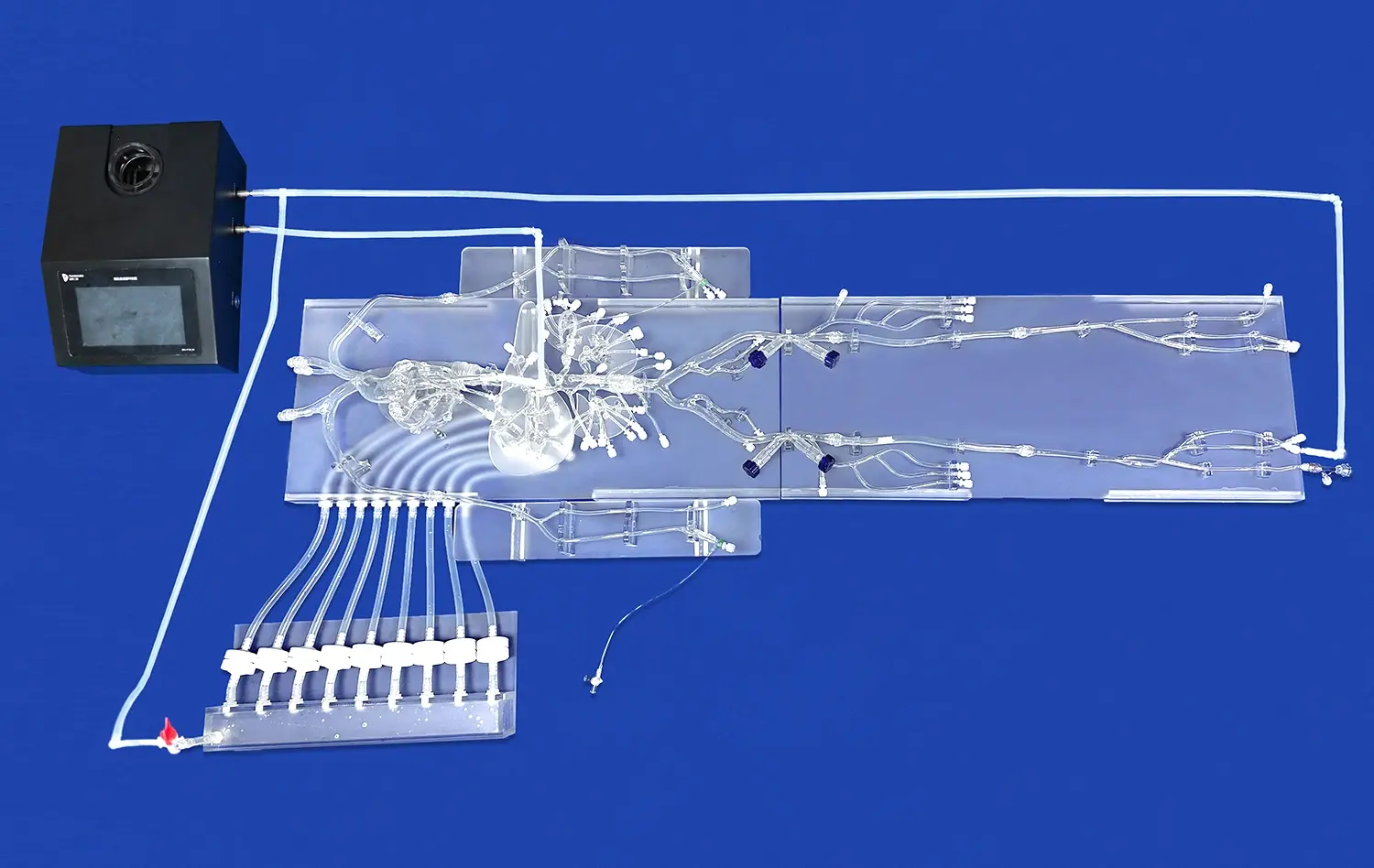
3D kidney models offer an unparalleled level of detail in representing renal anatomy. These models are typically created using high-resolution medical imaging data, such as CT or MRI scans, ensuring that they accurately reflect the intricate structures of the kidney. Surgeons can observe and interact with detailed representations of the renal cortex, medulla, collecting system, and vascular network. This level of detail allows for a comprehensive understanding of the spatial relationships between different anatomical structures, which is crucial for planning and executing complex surgical procedures.
Moreover, 3D kidney models can be customized to showcase specific anatomical variations or abnormalities, providing surgeons with exposure to a wide range of renal anatomies. This diversity in model types helps broaden surgeons' understanding of the potential anatomical challenges they may encounter during actual surgeries, thereby enhancing their preparedness and adaptability in the operating room.
Interactive Learning Experience
Unlike traditional 2D imaging or textbook illustrations, 3D kidney models offer an interactive learning experience. Surgeons can physically manipulate these models, rotating them to view the kidney from various angles and exploring its internal structures. This hands-on approach facilitates a deeper understanding of the kidney's three-dimensional structure and spatial relationships, which is particularly beneficial for visualizing complex surgical approaches.
Additionally, some advanced 3D kidney models incorporate flexible materials that mimic the texture and consistency of real renal tissue. This feature allows surgeons to practice incisions and suturing techniques, further enhancing their tactile understanding of kidney anatomy. The ability to interact with these models in a tactile manner helps reinforce anatomical knowledge and improves spatial awareness, both of which are crucial skills for successful renal surgeries.
Can 3D Kidney Models Simulate Complex Renal Pathologies for Surgical Practice?
Replication of Pathological Conditions
3D kidney models excel in their ability to simulate a wide array of renal pathologies, providing surgeons with valuable opportunities for targeted practice. These models can accurately replicate conditions such as renal tumors, cysts, stones, and congenital abnormalities. By incorporating patient-specific imaging data, it's possible to create models that precisely mirror the unique pathological features of individual cases. This level of customization allows surgeons to rehearse procedures on models that closely resemble the actual patient's kidney, enhancing their preparedness for the specific challenges they may face during surgery.
The ability to simulate complex pathologies extends beyond mere visual representation. Advanced 3D printing techniques can produce models with varying densities and textures, mimicking the feel of different types of renal tissues and pathologies. For instance, models can be designed to replicate the firmness of a tumor or the fragility of a cystic structure, providing a realistic tactile experience that is crucial for developing the fine motor skills required in delicate renal surgeries.
Scenario-Based Training
3D kidney models enable the creation of scenario-based training exercises that simulate real-world surgical challenges. These scenarios can be designed to progressively increase in complexity, allowing surgeons to gradually build their skills and confidence. For example, a training program might start with simple cyst removal exercises and progress to more complex tumor resections or partial nephrectomies.
These models also facilitate the practice of decision-making skills in a low-stakes environment. Surgeons can experiment with different approaches to treating complex pathologies, assessing the potential outcomes of various surgical techniques without risking patient safety. This type of experiential learning is invaluable in developing the critical thinking and problem-solving skills essential for managing unexpected complications during actual surgeries.
What Are the Benefits of Using 3D Kidney Models for Hands-On Surgical Simulation?
Improved Surgical Planning
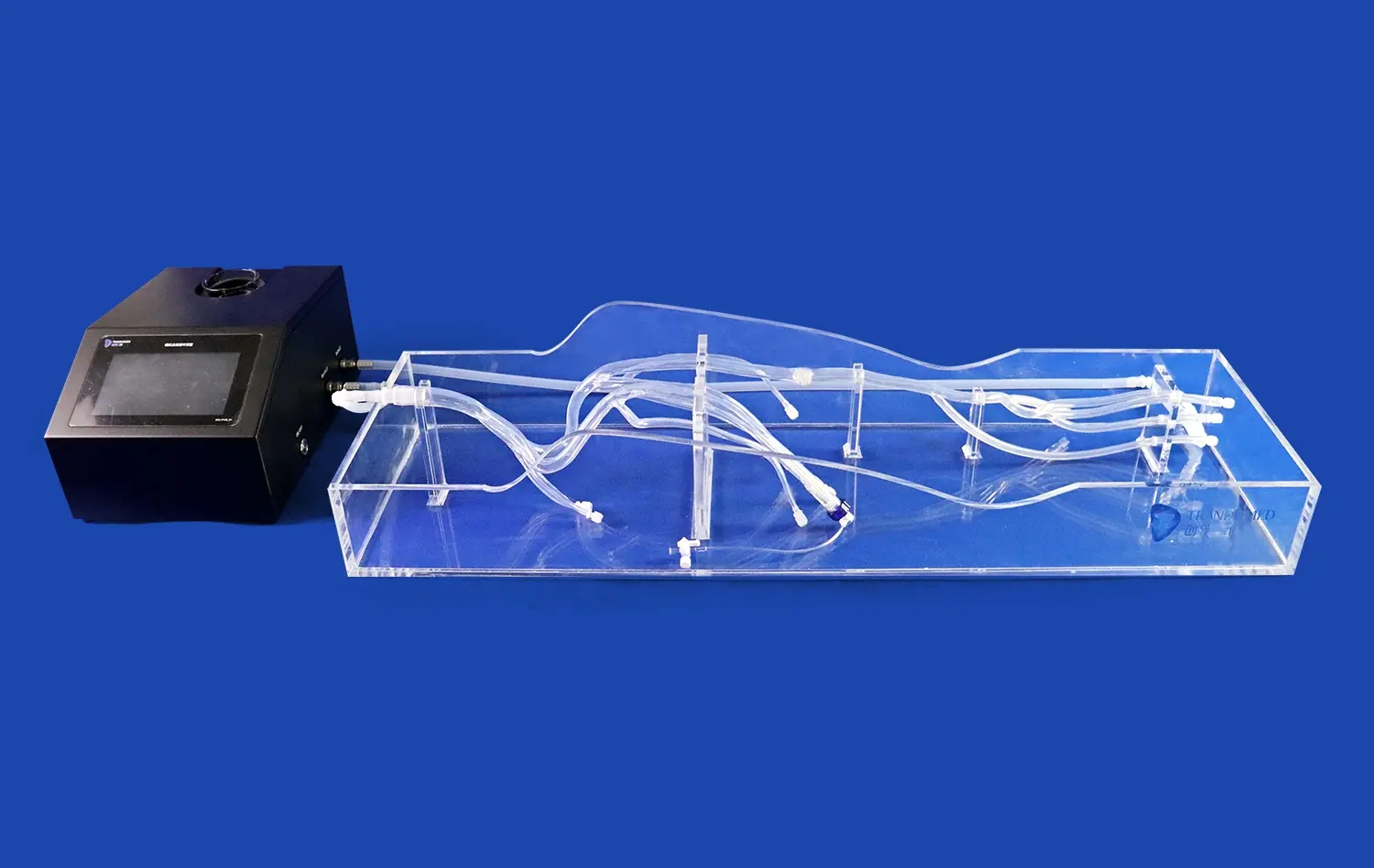
3D kidney models serve as powerful tools for preoperative planning, allowing surgeons to meticulously strategize their surgical approach. By studying patient-specific models, surgeons can identify potential challenges, such as unusual vascular arrangements or the proximity of tumors to critical structures. This advanced planning helps in determining the optimal surgical technique, reducing the risk of complications, and potentially shortening operative times.
Furthermore, these models facilitate better communication within the surgical team. Surgeons can use the models to explain the planned procedure to colleagues, anesthesiologists, and operating room staff, ensuring everyone is aligned on the surgical strategy. This improved communication can lead to more efficient teamwork during the actual surgery, ultimately benefiting patient outcomes.
Enhanced Skill Development
Hands-on practice with 3D kidney models accelerates the development of crucial surgical skills. Surgeons can repeatedly perform complex procedures, honing their techniques without the time constraints or pressures associated with live surgeries. This repetitive practice is particularly beneficial for mastering challenging techniques such as laparoscopic or robotic-assisted renal surgeries.
The use of these models also allows for objective assessment and feedback on surgical performance. Institutions can implement standardized training programs using 3D models, enabling consistent evaluation of surgeons' skills and progress. This structured approach to skill development ensures that surgeons achieve a high level of competency before performing procedures on actual patients, thereby enhancing patient safety and surgical outcomes.
Conclusion
3D kidney models have emerged as a transformative tool in the training of renal surgeons, offering unparalleled opportunities for anatomical understanding, pathology simulation, and hands-on surgical practice. These models bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, enabling surgeons to develop and refine their skills in a risk-free environment. By providing detailed anatomical representations, simulating complex pathologies, and facilitating scenario-based training, 3D kidney models contribute significantly to improved surgical planning, enhanced skill development, and ultimately, better patient outcomes. As technology continues to advance, the integration of 3D models in surgical education is poised to play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of renal surgery.
Contact Us
For more information about our advanced 3D kidney models and how they can enhance your surgical training program, please contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com. Let us help you take your renal surgery skills to the next level with our state-of-the-art 3D printed medical simulators.
References
Zhang, Y., et al. (2019). "Application of 3D printing technology in kidney surgery: A systematic review." Journal of Endourology, 33(5), 356-368.
Porpiglia, F., et al. (2018). "Three-dimensional printing of models for surgical planning in patients with primary posterior pelvic tumors." European Urology Focus, 4(3), 414-421.
Bernhard, J.C., et al. (2016). "Personalized 3D printed model of kidney and tumor anatomy: a useful tool for patient education." World Journal of Urology, 34(3), 337-345.
Wake, N., et al. (2017). "Patient-specific 3D printed and augmented reality kidney and prostate cancer models: impact on patient education." 3D Printing in Medicine, 3(1), 1-8.
Komai, Y., et al. (2016). "Patient-specific 3-dimensional printed kidney designed for '4D' surgical navigation: A novel aid to facilitate minimally invasive off-clamp partial nephrectomy in complex renal tumors." Urology, 91, 226-233.
Silberstein, J.L., et al. (2014). "Physical models of renal malignancies using standard cross-sectional imaging and 3-dimensional printers: A pilot study." Urology, 84(2), 268-273.

 (SJ001D)_1734504338727.webp)