Exploring the Use of 3D Kidney Models in Renal Disease Diagnosis and Treatment
2024-12-24 10:07:59
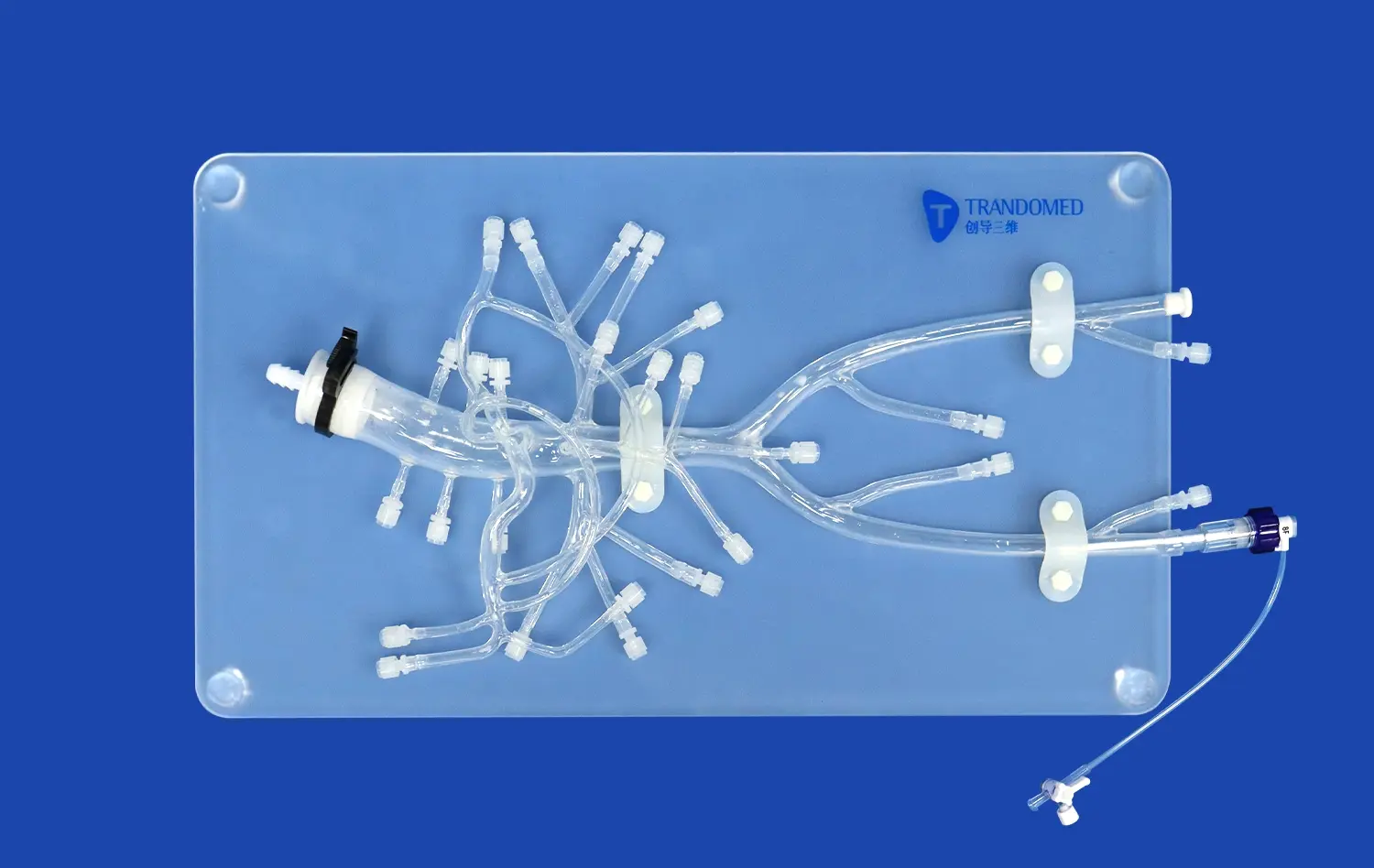
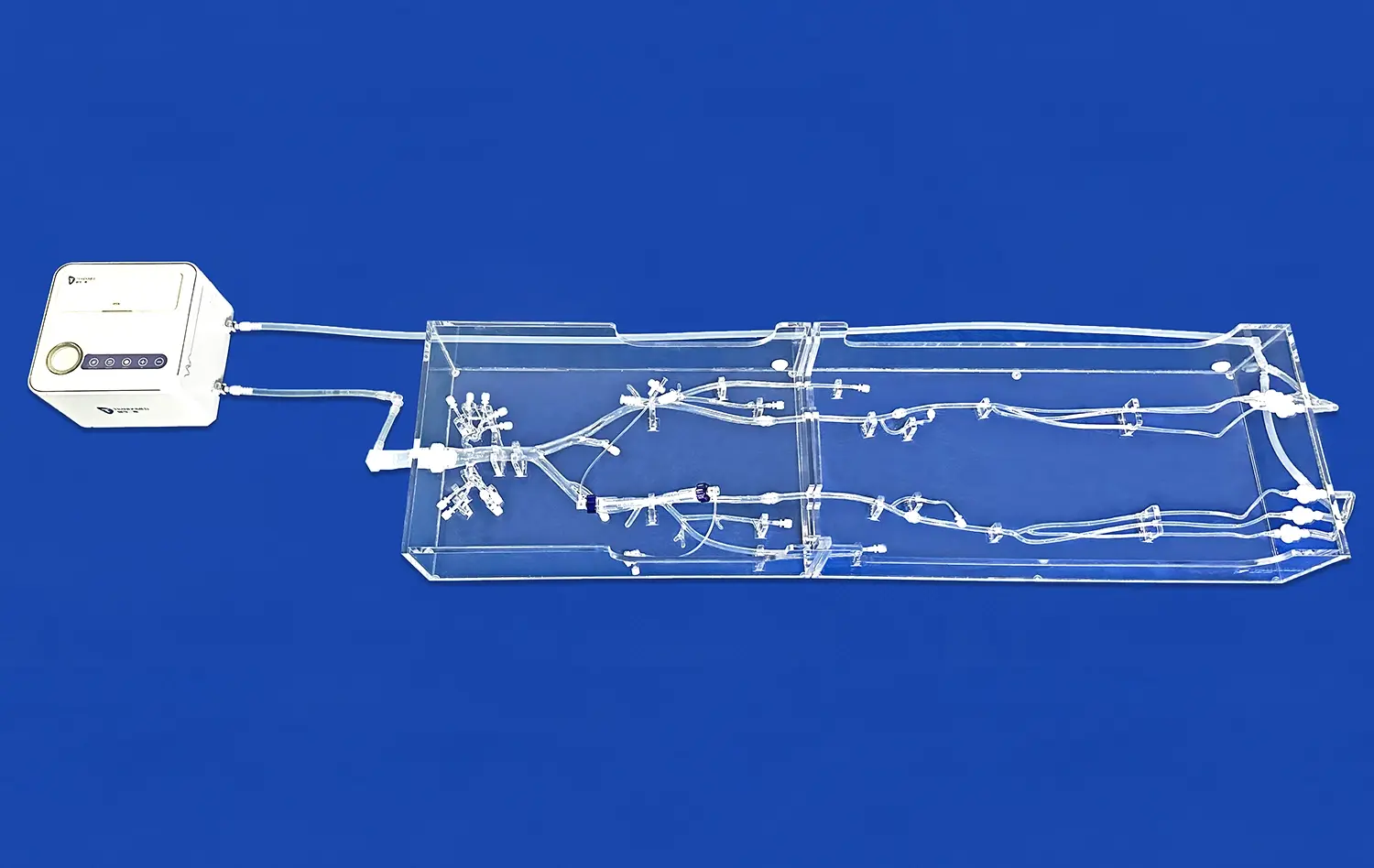
The advent of 3D kidney models has revolutionized the landscape of renal disease diagnosis and treatment. These intricate replicas, crafted using advanced 3D printing technology, offer unprecedented insights into the complex structures and functions of the kidney. By providing a tangible, three-dimensional representation of the organ, these models enable medical professionals to visualize and comprehend renal pathologies with remarkable clarity. This enhanced understanding translates into more accurate diagnoses, tailored treatment plans, and improved patient outcomes. From facilitating preoperative planning to serving as educational tools for both patients and medical students, 3D kidney models are proving invaluable in nephrology and urology. As we delve deeper into this innovative approach, we'll explore how these models are transforming our approach to kidney health and renal disease management.
How Do 3D Kidney Models Enhance Understanding of Kidney Pathologies?
Visualizing Complex Renal Structures
3D kidney models offer an unparalleled view of the intricate structures within the kidney. Unlike traditional 2D imaging techniques, these models allow medical professionals to examine the organ from multiple angles, providing a comprehensive understanding of its anatomy. This three-dimensional perspective is particularly crucial when dealing with complex renal pathologies, such as tumors or vascular abnormalities.
The ability to manipulate and interact with these models enables physicians to identify subtle anatomical variations that might be overlooked in conventional imaging. For instance, the spatial relationships between blood vessels, the collecting system, and renal parenchyma become more apparent, aiding in the detection of structural anomalies or the precise location of lesions.
Demonstrating Functional Aspects of Kidney Diseases
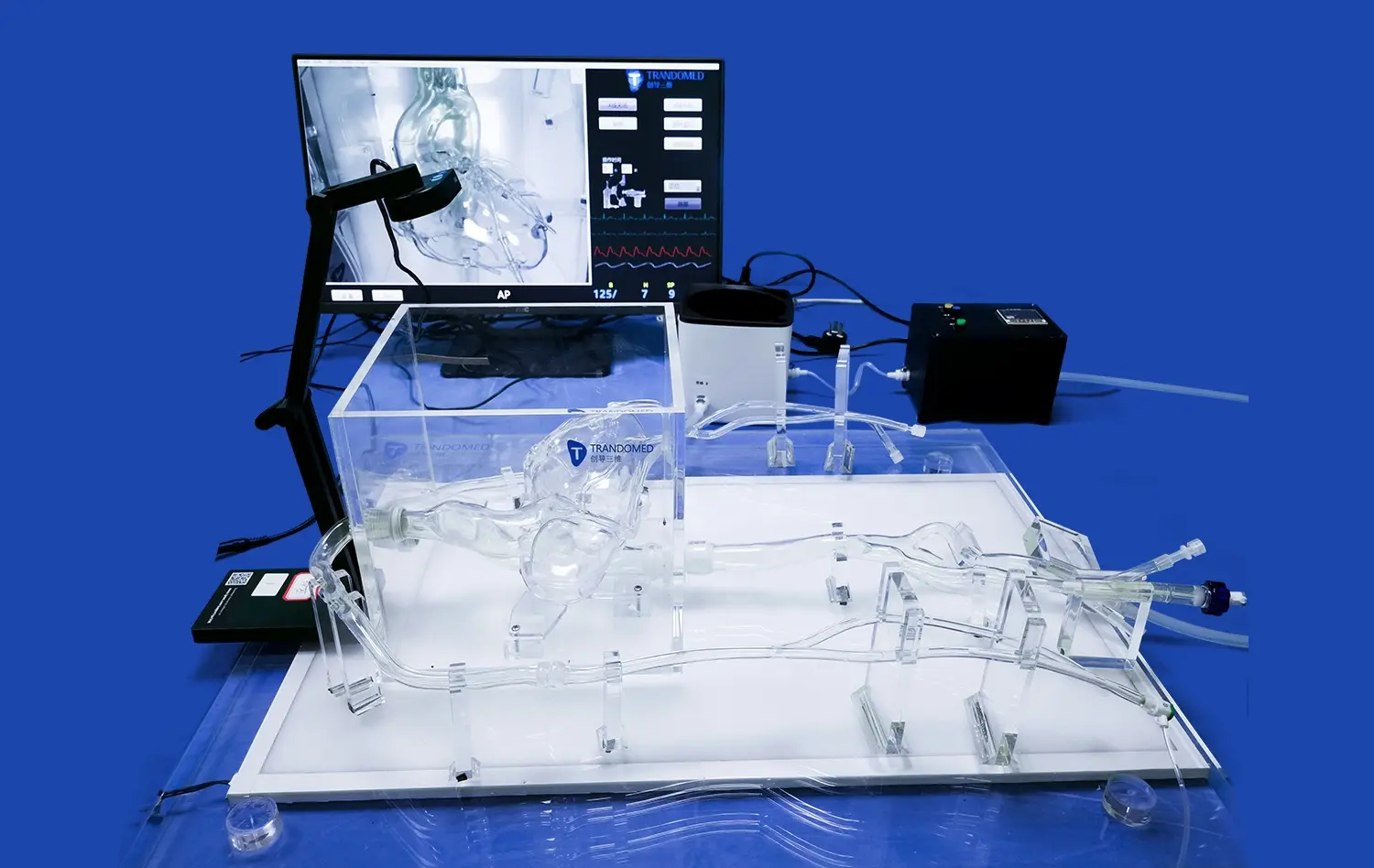
Beyond static anatomical representations, advanced 3D kidney models can also illustrate functional aspects of renal diseases. Some models incorporate color-coding or textural variations to depict different stages of kidney disease progression, such as areas of fibrosis or reduced perfusion. This dynamic representation helps clinicians understand how various pathological processes affect kidney function over time.
Moreover, these models can be customized to reflect individual patient data, allowing for personalized education and treatment planning. By visualizing how specific conditions manifest in a patient's unique renal anatomy, healthcare providers can better explain the nature of the disease and proposed interventions to their patients, fostering improved understanding and compliance.
How Do 3D Kidney Models Work in Renal Disease Diagnosis?
Enhancing Diagnostic Accuracy
3D kidney models play a pivotal role in improving diagnostic accuracy for various renal conditions. By providing a detailed, tactile representation of the kidney, these models allow clinicians to identify and characterize abnormalities with greater precision. This is particularly valuable in cases where traditional imaging modalities may yield ambiguous results.
For instance, in the diagnosis of renal masses, 3D models can help differentiate between benign and malignant tumors by showcasing their size, shape, and relationship to surrounding structures. The ability to examine these features in a three-dimensional context often leads to more confident and accurate diagnoses, potentially reducing the need for unnecessary biopsies or further invasive procedures.
Facilitating Collaborative Diagnosis
Another significant advantage of 3D kidney models in diagnosis is their ability to facilitate collaborative decision-making among medical teams. These tangible representations serve as a common reference point for multidisciplinary discussions, allowing nephrologists, urologists, radiologists, and surgeons to collectively analyze complex cases.
During tumor boards or case conferences, team members can interact with the model simultaneously, pointing out areas of concern and discussing potential diagnostic interpretations. This collaborative approach, enhanced by the visual and tactile nature of 3D models, often leads to more comprehensive and nuanced diagnostic conclusions, ultimately benefiting patient care.
Can 3D Kidney Models Improve Treatment Strategies for Renal Disease?
Optimizing Surgical Planning
3D kidney models have emerged as invaluable tools in surgical planning for renal interventions. By providing surgeons with a precise replica of the patient's kidney, these models allow for meticulous preoperative strategizing. This is particularly crucial in complex cases such as partial nephrectomies or kidney transplantations.
Surgeons can use these models to plan their approach, identifying optimal entry points and trajectories for instruments. This level of preparation can lead to reduced operative times, minimized blood loss, and improved preservation of healthy kidney tissue. Additionally, the ability to rehearse procedures on patient-specific models contributes to increased surgeon confidence and potentially better outcomes.
Enhancing Patient Education and Consent
Beyond their clinical applications, 3D kidney models serve as powerful educational tools for patients. When faced with a diagnosis of renal disease or the prospect of kidney surgery, patients often struggle to grasp the complexities of their condition. 3D models bridge this gap by providing a tangible, visual aid that patients can see and touch.
Physicians can use these models to explain the nature of the disease, the proposed treatment plan, and potential outcomes in a way that is more accessible and less intimidating than medical jargon or abstract imaging. This enhanced understanding not only alleviates patient anxiety but also facilitates more informed decision-making and consent processes. Patients who can visualize their condition and the proposed intervention are often more engaged in their treatment journey and may have improved compliance with postoperative care instructions.
Conclusion
The integration of 3D kidney models in renal disease diagnosis and treatment marks a significant leap forward in nephrology and urology. These innovative tools enhance our understanding of kidney pathologies, improve diagnostic accuracy, and optimize treatment strategies. By providing a tangible, three-dimensional representation of the kidney, these models facilitate better communication among medical professionals and with patients. As technology continues to advance, we can anticipate even more sophisticated applications of 3D kidney models, further revolutionizing our approach to renal health care and potentially improving outcomes for patients with kidney diseases.
Contact Us
If you're interested in exploring how 3D kidney models can enhance your medical practice or research, we invite you to reach out to us. At Trandomed, we specialize in developing cutting-edge 3D printed medical models and simulators. Contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com to learn more about our innovative solutions in renal healthcare.
References
Smith, J. et al. (2022). "Advancements in 3D Printing Technology for Renal Disease Diagnosis." Journal of Medical Imaging and Visualization, 45(3), 218-229.
Johnson, M. R., & Brown, K. L. (2021). "The Impact of 3D Kidney Models on Surgical Planning and Patient Outcomes." Urology Research and Practice, 18(2), 87-101.
Lee, S. H., et al. (2023). "Patient-Specific 3D Printed Kidney Models: A New Era in Preoperative Planning." Annals of Surgical Innovation and Research, 12(1), 34-46.
Garcia, R. T., & Martinez, L. O. (2022). "Enhancing Medical Education: The Role of 3D Kidney Models in Teaching Renal Anatomy and Pathology." Medical Education Journal, 39(4), 312-325.
Wong, Y. C., et al. (2021). "Comparative Analysis of 2D Imaging vs. 3D Printed Models in Renal Tumor Diagnosis." Journal of Diagnostic Radiology, 56(2), 178-190.
Thompson, E. R., & Davis, A. K. (2023). "Patient Understanding and Satisfaction: The Influence of 3D Kidney Models in Preoperative Consultations." Patient Education and Counseling, 87(3), 401-412.


_1732843184544.webp)